Introduction to Fine Motor, Speech & Social Skills
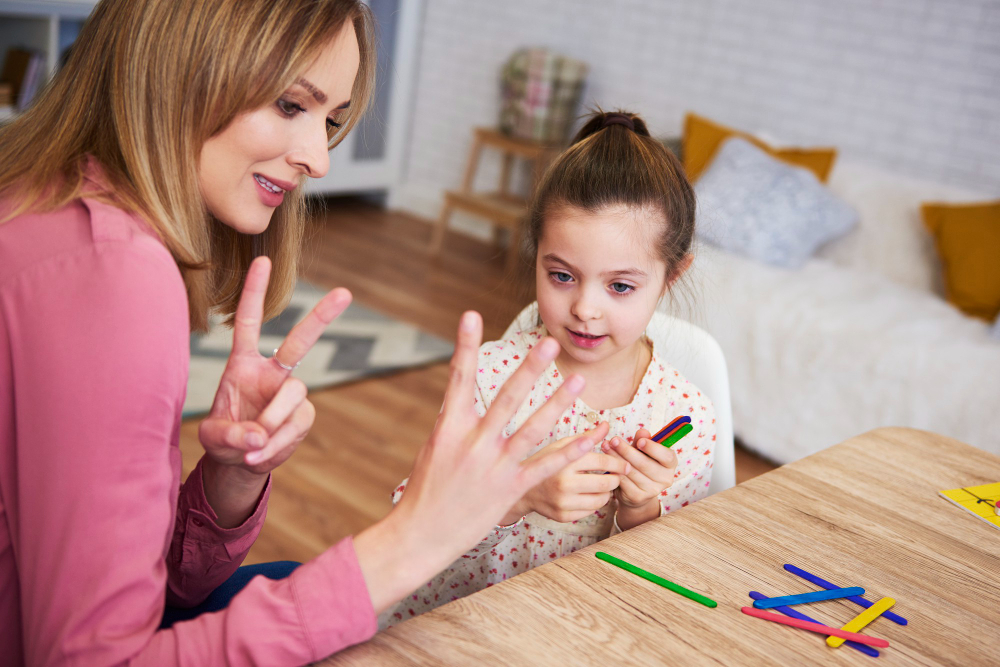
Fine motor, speech & social skills are important for every child’s growth. These skills help children move their hands, talk, and connect with others. For example, fine motor skills let kids hold a pencil or button a shirt. Speech and language milestones show how well a child can talk and understand words. Social skills in children help them make friends and share feelings. Because these skills shape learning and daily life, it is important to notice any delays early. Early intervention for developmental delays can make a big difference. Families should know the signs and seek support for speech and motor skills when needed.
Common Signs and Symptoms
Many children develop skills at their own pace. However, some signs may show a child needs extra help. For instance, you may notice:
Additionally, children may avoid group activities or get upset easily. If you see these signs, talk to a specialist. Early support can help children reach their full potential.
Causes and Risk Factors
There are many reasons why children may have trouble with fine motor, speech & social skills. Some common causes include:
Sometimes, the cause is not clear. But, knowing the risk factors helps families watch for early signs. According to the CDC, early detection leads to better outcomes for children.
Diagnosis and Assessment Methods
Doctors and specialists use different tools to check fine motor, speech & social skills. First, they may ask about your child’s milestones and daily activities. Next, they might use checklists or simple tests. For example, they may watch your child draw, speak, or play with others. Sometimes, hearing and vision tests are needed. In some cases, a team of experts, such as speech therapists or occupational therapists, will help. Early assessment is key, so do not wait if you have concerns.
Treatment and Support Strategies
There are many ways to help children improve their fine motor, speech & social skills. Treatment plans depend on each child’s needs. Common support strategies include:
Moreover, regular practice and encouragement help children gain confidence. Early intervention for developmental delays often leads to better progress.
Tips for Families and Caregivers
Families play a big role in supporting children. Here are some helpful tips:
Additionally, stay patient and keep routines simple. If you need help, reach out to local support services or schools. Many areas offer free screenings and early intervention programs.
Prevention and Early Intervention
While not all delays can be prevented, early action helps. For example, regular check-ups let doctors spot problems sooner. Also, creating a safe and rich learning environment at home supports growth. If you notice delays, seek help right away. Early intervention for developmental delays can improve speech and motor skills. In many cities, families can find local programs and resources. Ask your doctor about services in your area.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In summary, fine motor, speech & social skills are key for every child’s success. Watching for signs and acting early can make a big difference. If you have concerns, do not wait. Consult a qualified specialist for personalized guidance on fine motor, speech, and social skills development.